Central Pacific Railroad
| Central Pacific Railroad | |
 | |
| Típus | közlekedési társaság |
| Jogelőd |
|
| Alapítva | 1861. június 28. |
| Megszűnt | |
| Jogutód | Southern Pacific Transportation Company |
| Székhely | Sacramento |
| Forma | részvénytársaság |
A Wikimédia Commons tartalmaz Central Pacific Railroad témájú médiaállományokat. | |
| Sablon • Wikidata • Segítség | |
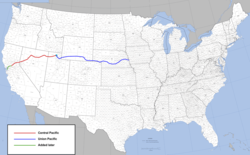
A Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR) egy vasúti társaság volt, amelyet az amerikai kongresszus 1862-ben alapított, hogy a kaliforniai Sacramentótól keletre vasutat építsen, hogy befejezze az "első transzkontinentális vasútvonal" nyugati részét Észak-Amerikában. Az 1861-ben alapított CPRR 1885-ben szüntette be működését, amikor a Southern Pacific Railroad bérbeadott vonalként felvásárolta.
A csendes-óceáni vasút 1855-ös felmérésének befejezését követően több, transzkontinentális vasút építésére irányuló országos javaslat is elbukott a rabszolgasággal kapcsolatos politikai viták által felemésztett energia miatt. Dél 1861-es elszakadásával a Republikánus Párt modernizálói kerültek az amerikai kongresszus élére. Ők 1862-ben törvényt fogadtak el, amely engedélyezte a központi vasútvonalat, finanszírozásuk földtámogatások és kormányzati vasúti kötvények formájában történt, amelyeket végül mind visszafizettek kamatostul.[1] 1862-ben a kormány és a vasutasok egyaránt részesültek a földtámogatások megnövekedett értékéből, amelyet a vasutak fejlesztettek ki. 1862-ben a vasút megépítése a kormány számára is biztosította a gazdaságos posta, csapatok, hadianyagok és a közraktárak biztonságos és gyors szállítását.[2]
Története[szerkesztés]
A Theodore Judah által tervezett Central Pacific Railroadot a Kongresszus 1862-ben engedélyezte. Judah és a "The Big Four" (akik magukat "The Associates"-nek nevezték) 1861-ben alapította: Leland Stanford, Collis Potter Huntington, Charles Crocker és Mark Hopkins Jr., Sacramento, Kalifornia üzletemberei. Stanfordot választották elnöknek (egyúttal kormányzónak is megválasztották), Huntingtont alelnöknek, aki az adománygyűjtésért és a beszerzésekért felelt, Hopkinst pedig pénztárosnak. Crocker volt a felelős az építkezésért, amely hivatalosan 1863-ban kezdődött, amikor Sacramentóban lefektették az első síneket.
Az építkezés 1865-ben indult meg komolyan, amikor James Harvey Strobridge, az építőmunkások vezetője Crocker javaslatára felvette az első kantoni emigráns munkásokat. Az építőbrigád 1868-ra 12 000 kínai munkással nőtt, amikor is áttörték a Donner-csúcsot, és a teljes munkásság nyolcvan százalékát tették ki.[3][4] 1869. május 10-én ütötték be az "arany sínszeget", amely a nyugati vasutat a Utah állambeli Promontorynál összekötötte a Union Pacific Railroaddal.[5] 1869-ben lehetővé vált nyolc nap alatt a tengerparttól a tengerpartig tartó vonatközlekedés, felváltva a hónapokig tartó tengeri utakat és a hosszadalmas, veszélyes szekérkaravánokkal való utazást.
1885-ben a Central Pacific Railroadot a Southern Pacific Company bérbe vett vonalként megvásárolta. Gyakorlatilag a CPRR 1959-ig maradt vállalati egység, amikor hivatalosan beolvadt a Southern Pacificbe. (1899-ben szervezték át Central Pacific "Railroad" néven.) Az eredeti útjogot ma a Union Pacific ellenőrzi, amely 1996-ban megvásárolta a Southern Pacificet.
A Union Pacific-Central Pacific (Southern Pacific) fővonala a történelmi Overland Route-t követte a nebraskai Omahától a San Francisco-öbölig.
A vasút építéséhez a kínai munkaerő volt a legfontosabb forrás.[6] 1865 februárjában a nyugati vasutasok többsége kínai volt, mivel a fehér munkások nem voltak hajlandók elvégezni a veszélyes munkát.[7] 1865 februárjában a Central Pacific Railroad próbaüzemben ötven kantoni emigráns munkást vett fel, és hamarosan egyre több kantoni emigránst alkalmaztak. A munkakörülmények kemények voltak, és a kínaiak kevesebbet kaptak, mint fehér társaik. A kínai munkásoknak havonta harmincegy dollárt fizettek, és míg a fehér munkások ugyanennyit kaptak, nekik szállást és ellátást is biztosítottak.[8] Idővel a CPRR felismerte az alacsony bérért alkalmazott jó munkások előnyeit: "A kínai munkaerő bizonyult a Central Pacific megmentőjének."[9]:30
Irodalom[szerkesztés]
- Ambrose, Stephen E.. Nothing Like It in the World: The Men Who Built the Transcontinental Railroad, 1863–1869. New York: Simon & Schuster (2000). ISBN 0-684-84609-8
- Bain, David Haward. Empire Express: Building the First Transcontinental Railroad. New York: Viking (1999). ISBN 0-670-80889-X
- Beebe, Lucius. The Central Pacific and Southern Pacific Railroads. Berkeley, CA: Howell-North Books (1963)
- Chang, Gordon. Ghosts of Gold Mountain. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt (2020) Profiles how 20,000 Chinese railroad workers lived and worked while building the Central Pacific over Donner Pass. Shows changing attitudes of CPRR officials who employed the Chinese.
- Cooper, Bruce C.. Riding the Transcontinental Rails: Overland Travel on the Pacific Railroad 1865–1881. Philadelphia: Polyglot Press (2005). ISBN 1-4115-9993-4
- Cooper, Bruce Clement. The Classic Western American Railroad Routes. New York: Chartwell Books/Worth Press (2010). ISBN 978-0-7858-2573-9
- Daggett, Stuart. Chapters on the History of the Southern Pacific. New York: The Ronald Press (1922) „chapters southern pacific.”
- Evans, Cerinda W.. Collis Potter Huntington (2 vols.) [archivált változat]. Newport News, Va.: Mariners' Museum (1954). Hozzáférés ideje: 2021. szeptember 23. [archiválás ideje: 2011. június 4.]
- Fleisig, Heywood (1975). „The Central Pacific Railroad and the Railroad Land Grant Controversy”. Journal of Economic History 35 (3), 552–566. o. DOI:10.1017/s002205070007563x. Questions whether promoters of the Central Pacific Railroad were oversubsidized. Confirms the traditional view that subsidies were not an economic necessity because they "influenced neither the decision to invest in the railroad nor the speed of its construction." Notes that estimates of rate of return for the railroad developers using government funds range from 71% to 200%, while estimates of private rates of return range from 15% to 25%.
- Galloway, John Debo. The First Transcontinental Railroad: Central Pacific, Union Pacific [archivált változat]. New York: Simmons-Boardman (1950). Hozzáférés ideje: 2021. szeptember 23. [archiválás ideje: 2011. június 4.]
- Goldbaum, Howard, and Wendell Huffman. Waiting for the Cars: Alfred A. Hart's Stereoscopic Views of the Central Pacific Railroad, 1863–1869. Carson City: Nevada State Railroad Museum (2012)
- Griswold, Wesley. A Work of Giants: Building the First Trans-continental Railroad. New York: McGraw-Hill (1962)
- Klein, Maury. Union Pacific (3 vols.). Garden City, NY: Doubleday (1987). ISBN 0-385-17728-3
- Kraus, George. High Road to Promontory: Building the Central Pacific (Now the Southern Pacific) across the High Sierra. Palo Alto: American West Pub. Co. (1969)
- Kraus, George (1975). „Chinese Laborers and the Construction of the Central Pacific”. Utah Historical Quarterly 37 (1), 41–57. o. Shows how Chinese railroad workers lived and worked, and managed the finances associated with their employment. Concludes that CPRR officials who employed the Chinese, even those at first opposed to the policy, came to appreciate the reliability of this group of laborers. There are many quotations from accounts by contemporary observers.
- Lake, Holly (1994). „Construction of the CPRR: Chinese Immigrant Contribution”. Northeastern Nevada Historical Society Quarterly 94 (4), 188–199. o.
- Mercer, Lloyd J. (1970). „Rates of Return for Land-grant Railroads: the Central Pacific System”. Journal of Economic History 30 (3), 602–626. o. DOI:10.1017/S0022050700086241. Analyzes the impact of land grants from 1864 to 1890 on rates of return from investment in the Central Pacific Railroad. Results suggest that even without land grants, rates of return were high enough to induce investment. Also, land grants did not pay for the construction of the railroad. Land grants, however, did produce large social returns in western states by accelerating construction of the system.
- Mercer, Lloyd J. (1969). „Land Grants to American Railroads: Social Cost or Social Benefit?”. Business History Review 43 (2), 134–151. o. DOI:10.2307/3112269. Uses econometrics to determine the value of railroad land grants of the 19th century to the railroads and to society. The author summarizes and criticizes previous treatments of this subject, and discusses his own findings. Using the Central Pacific and the Union Pacific systems as the basis for his investigation, the author concludes that the railroad owners received unaided rates of return that substantially exceeded the private rate of return on the average alternative project in the economy during the same period. Thus, the projects were profitable, although contemporary observers expected that the roads would be privately unprofitable without the land grant aid. The land grants did not have a major effect, increasing the private rate of return only slightly. Nevertheless, he says the policy of subsidizing those railroad systems was beneficial for society since the social rate of return from the project was substantial and exceeded the private rate by a significant margin.
- Ong, Paul M. (1985). „The Central Pacific Railroad and Exploitation of Chinese Labor”. Journal of Ethnic Studies 13 (2), 119–124. o. Ong tries to resolve the apparent inconsistency in the literature on Asians in early California, with contradictory studies showing evidence both for and against the exploitation of Chinese labor by the CPRR, using monopsony theory as developed by Joan Robinson. Because CPRR set different wages for whites and Chinese (each group had different elasticities of supply) and used the two classes in different types of positions, the two groups were complementary, rather than interchangeable. Calculations thus show higher levels of exploitation of the Chinese than found in previous studies.
- Saxton, Alexander (1966). „The Army of Canton in the High Sierra”. Pacific Historical Review 35 (2), 141–151. o. DOI:10.2307/3636678.
- Tutorow, Norman E. (1970). „Stanford's Responses to Competition: Rhetoric Versus Reality”. Southern California Quarterly 52 (3), 231–247. o. DOI:10.2307/41170298. Leland Stanford and the men who ran the CPRR paid lip-service to the idea of free competition, but in practice sought to dominate competing railroad and shipping lines. Analyzing the period 1869–1893, the author shows how Stanford and his associates repeatedly entered into pooling arrangements to prevent competition, bought out competitors, or forced rivals to agree not to compete. He concludes that Stanford and his partners viewed laissez-faire as applicable only to government controls, and not to businessmen's destruction of competition within the system.
- White, Richard (2003). „Information, Markets, and Corruption: Transcontinental Railroads in the Gilded Age”. The Journal of American History 90 (1). DOI:10.2307/3659790.
- White, Richard. Railroaded: The Transcontinentals and the Making of Modern America. W. W. Norton & Company (2011. április 30.). ISBN 978-0-393-06126-0
- Williams, John Hoyt. A Great and Shining Road: The Epic Story of the Transcontinental Railroad. New York: Times Books (1988). ISBN 0-8129-1668-9
- „The Iron Road”. Neil Goodwin, Peace River Films. The American Experience. PBS. 1990. április 30.
- Best, Gerald M. Iron Horses to Promontory. New York: Golden West (1969)
További információk[szerkesztés]
- Central Pacific Railroad lawsuit and investigation documents, 1876-1887 at the California State Library.
- Guide to the Central Pacific Railroad Company Collection, 1861-1899 at California State Library.
- Central Pacific Railroad Photographic History Museum
- Railroads in California, handwritten report by L. M. Clement. Special Collections and Archives, The UC Irvine Libraries, Irvine, California.
Források[szerkesztés]
- ↑ Daggett, Stuart. Union Pacific, Railroad Reorganization. Harvard University Press, 256. o. (1908)
- ↑ CPRR.org: Pacific Railroad Act of 1862, §2. Cprr.org, 2009. szeptember 24. (Hozzáférés: 2014. január 17.)
- ↑ Workers of the Central Pacific Railroad Archiválva 2017. március 18-i dátummal a Wayback Machine-ben, PBS: The American Experience.
- ↑ George Kraus, "Chinese Laborers and the Construction of the Central Pacific," Utah Historical Quarterly, vol. 37, no. 1 (Winter 1969), pp. 41–57.
- ↑ Ceremony at "Wedding of the Rails," May 10, 1869 at Promontory Point, Utah. World Digital Library , 1869. május 10. (Hozzáférés: 2013. július 20.)
- ↑ The Chinese and the iron road: Building the transcontinental railroad. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press (2019. április 30.). ISBN 9781503608290
- ↑ Sayej, Nadja: 'Forgotten by society' – how Chinese migrants built the transcontinental railroad, 2019. július 18.
- ↑ A History of Asian Americans: Strangers From A Different Shore, Second, New York, NY: Little, Brown and Company, 84–86. o. (1989. április 30.). ISBN 978-0-316-83130-7
- ↑ Railroaded: The transcontinentals and the making of modern America. New York: W W Norton & Co (2011. április 30.). ISBN 9780393061260 „Chinese labor proved to be Central Pacific's salvation.”


